INTRODUCTION
Hip flexion movement occurs in an anterior direction around coronal axis, which full range through is approximately 120 degree.1 Hip flexion is necessary to complete a squat, forward bend, or even initiate the swing phase of gait.2-4 Due to various injuries and soft tissue shortening surrounding a hip joint, limited hip flexion may affect lumbo-pelvic position and motion, and have been implicated as one of the indicators to low back pain.5 Additionally, prolonged sitting and chronic lumbar flexion posturing, many individuals lack adequate hip flexion. These people will move into early lumbar flexion when attempting hip movements (forward bending or squatting).6
It is important to regain range of motion (ROM) in a joint is one of the first phases of injury rehabilitation in low back pain with limited hip flexion.7 Through rehabilitation period, it is necessary to measure hip flexion ROM to confirm patient’s progress and condition or therapeutic effectiveness.8 Previous studies reported that flexion of hip is tested in the supine position and normally 120 degree with knee flexed.9 For the accurate measurement of hip flexion ROM, if the anterior superior iliac spine begins to move, the movement is stopped as pelvic rotation is occurring rather than hip flexion.8 However, we have difficulties of preventing or detecting the motion of lumbo-pelvic motion through traditional testing.
A pressure biofeedback unit (PBU) is made up of an inflatable plastic bag that is combined with a pressure gage displaying feedback on pressure for spine stabilization. To monitor stabilization of the lumbo-pelvic during exercise, a PBU has been commonly used in various biofeedback methods.10-13 However, a PBU has not been used to stabilize the lumbar during measurement of hip flexion ROM. If PBU is used for hip flexion ROM measurement to detect the motion of lumbo-pelvic, a net hip flexion angle without compensatory motion of lumbo-pelvic can be measured. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to investigate the difference between measurement of hip flexion ROM with lumbo-pelvic stabilization (HFwLS) and hip flexion ROM without lumbo-pelvic stabilization (HFwNLS), and to identify the test-retest reliability of HFwLS.
METHODS
21 students at Yonsei University participated and 41 legs recruited in this study (A date of one side leg has been lost). General characteristics of subjects are shown in Table 1. Inclusion criteria included no history of neurological disease, arthritis, connective tissue disorder, or hip joint injury or surgery. Exclusion criteria consisted of reported hip joint pain at the time of data collection, recent hip joint surgery for which the participant was still receiving care, or ongoing hip joint rehabilitation program. Before the study, the principal tester explained the experimental protocol to the subjects in detail. All subjects signed an informed consent form, and this study was approved by the Yonsei University Wonju Institutional Review Board (approval number: 1041849-201701-BM-008-02).
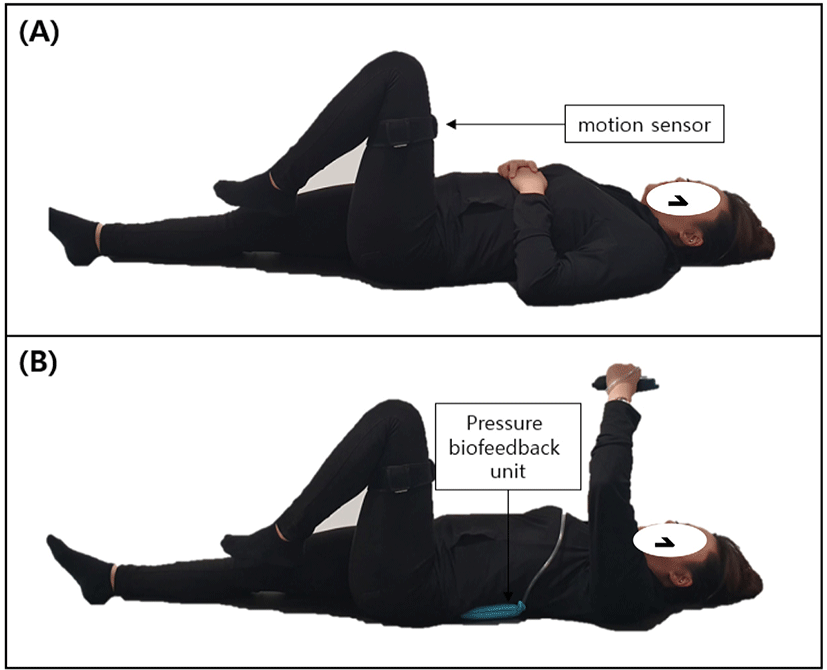
Hip flexion ROM was measured using Smart KEMA motion sensor (KOREATECH Co, Ltd, Seoul, Korea). The inertial measurement unit (IMU) contained a tri-axillar gyroscope, a magnetometer, and an accelerometer. Data from the motion sensor were recorded at a 25-Hz sampling frequency and transmitted to an Android tablet running Smart KEMA software. The one sensor attached to the midline of the lateral midline of the thigh using an adjustable belt. The PBU (Stabilizer, Chattanooga Group Inc., Hixson, TN, USA) was used to detect the motion of lumbo-pelvic. The PBU is an inflatable air-filled pressure sensor that is placed behind the subject’s lumbar spine.
Before the measurement, the subjects were instructed to perform measurement HFwNLS and HFwLS. For measurement of HFwNLS, the subject flexes the hip joint of the measurement side in the supine position (Figure 1A). During HFwLS, the subject flexes the hip joint of the measurement side in the supine position with maintaining initial pressure of PBU (Figure 1B). PBU is placed on the lumbar spine of the subject in supine position, and the initial value is set to 40mmHg. Changes in the PBU pressure during hip flexion ROM movement reflect the lumbo-pelvic motion, resulting in uncontrolled movement and excessive hip flexion ROM.
SPSS version 23.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for the statistical analyses, which was treated as a de-scriptive analysis (i.e., using means and standard deviation; SD). The Shapiro-Wilk test was used to check the data normality. Paired t-tests were conducted to compare differences between measurement of HFwNLS and HFwLS. Intra-class correlation coefficients [ICCs (3,1)] were used to determine the test-retest reliability of HFwLS. The test-retest reliability was calculated across results from the test sessions. Degree of reliability bases on ICCs was defined using the following criteria: .69 or less=poor, .70–.79= moderate, .80–.89=good, and .90–.99=excellent.14
RESULTS
The mean and SD values of measurement of hip flexion ROM and HFwLS are presented in Table 2. There are signifi-cant different between HFwNLS and HFwLS (t=10.04; p<0.01). And the test-retest ICC of the HFwLS was 0.971 (CI range from 0.95–0.99) between two session (Table 3).
| Measurement of hip flexion ROM | HFwLS | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angle | 124.70±12.89 | 104.61±15.23 | 10.04 | <0.01 |
| ICC (95% CI) | SEM (°) | MDD95 (°) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HFwLS | 0.97 | 2.59 | 7.19 |
DISCUSSION
Hip joint range of motion (ROM) is a basic clinical parameter for diagnosing hip diseases, such as osteoarthritis or femoroacetabular impingement, and for monitoring the efficacy of a treatment.15 Various measurement tools such as goniometer, inclinometer, and electromagnetic sensor used to measure hip joint ROM. These measurement have a difficulties for corrective measure by uncontrolled lumbo-pelvic movement, especially hip flexion ROM. For corrective measurement, it necessary to control or stabilize lumbo-pelvic motion. This study investigated the effects of lumbar stabilization on hip flexion ROM measurement.
Our study showed that the HFwLS was significantly in lower than HFwNLS. And test-retest ICC of the HFwLS was excellent between first and second measurement. There are possible explanations for our results. During the mea-surement of the HFwNLS, the hip flexion ROM value is accompanied by lumbo-pelvic motion. Therefore, accurate hip flexion ROM measurements were not made because of compensatory movements of lumbo-pelvic part. In the HFwLS, the hip flexion ROM could be measured with minimal lumbo-pelvic motion due to lumbo-pelvic stabilization using PBU. Lumbo-pelvic stabilization minimizes the factors affecting hip flexion ROM measurement, resulting in high measurement reliability.
Previous study reported that hip flexion measurement using a goniometer can be attributed to pelvic tilt, leading to an immense misinterpretation of this movement due to the insensitivity of manual goniometers for secondary pelvic movement.16 Elson and Aspinall suggested an alternative method for measuring hip flexion ROM by palpating the lumbosacral junction to allow early identification of lumbar spine flexion which accompanies hip flexion.17 During hip flexion ROM measurement, control or stabilization of lumbo-pelvic motion is difficult because it is difficult to detect lumbo-pelvic motion. For this reason, feedback information or tools are commonly used. A PBU is a non-invasive method that is economical, and it can be easily used anywhere since it is portable.18 Furthermore, a PBU has been used to monitor the motion of the lumbo-pelvic region.19-20 Therefore, lumbo-pelvic stabilization using a PBU is important considerations for precise measurement and may help to minimize measurement error during hip flexion ROM measurement. We believe that using a digital measuring device and PBU rather than a goniometer measurement without lumbo-pelvic stabilization improves the accuracy of the measurement in our study.
The present study had limitations. First, the generalization of the present study is limited because our subjects were young and small sample size. Therefore, further research is needed to examine in different age group. Additionally, other hip joint ROM is needed to examine for identifying the effectiveness of lumbo-pelvic stabilization on hip joint ROM. Second, we did not measure abnormal or compensatory movement for lumbo-pelvic motion. Further study is needed to examine the kinematic data for lumbo-pelvic motion.
CONCLUSIONS
The present study examined the effects of lumbo-pelvic stabilization on hip flexion ROM measurement. Based on the results, we suggested that the lumbo-pelvic stabilization could be provided for accurate or reliable measurement of hip flexion ROM measurement without compensatory lumbo-pelvic motion. This study provides useful information that can help physical therapist and health care related experts to examine accurate or reliable ROM measurement.







